- Achieving Excellence in Accounting: Lessons for Successful Professionals
- Kasra Dash Opens TaxBite Accountants Manchester – Lower Byrom St, Manchester M3 4AL
- CPA John Savignano on the 15 Traits Accountants Need To Succeed
- 360 ACCOUNTANTS ADDRESS HUGE FINANCIAL BURDEN FACING BUSINESSES
- Want to find the correct accountant for your business?
- YORKSHIRE ACCOUNTANTS ANNOUNCE NEW WEALTH MANAGEMENT PARTNERSHIP
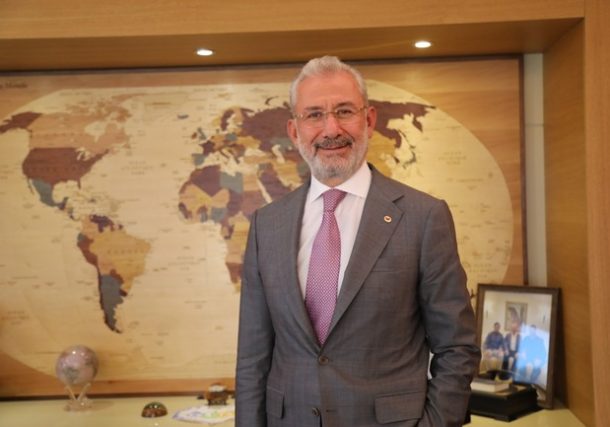
Tosçelik Spiral Boru, an esteemed division of Tosyalı, Türkiye’s dominant …
Custom backgrounds for your office team are not difficult to …
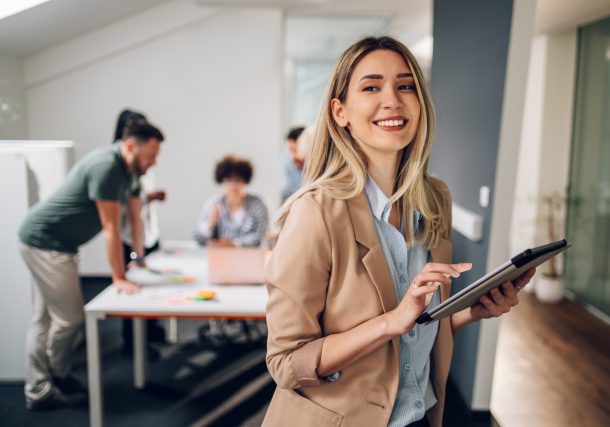
Change is a constant in today’s dynamic business landscape, and …
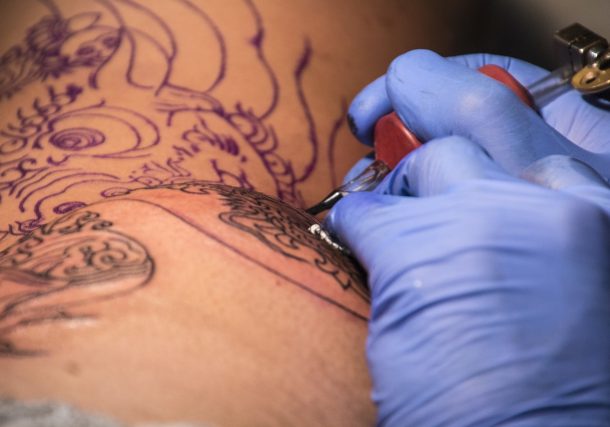
Amsterdam, 16-4-2024 – Tattoo culture has long been thriving in …
Technology
Business
Health
Lifestyle
Recent News
View AllTosçelik Spiral Boru, an esteemed division of Tosyalı, Türkiye’s dominant steel producer and the leading pipe manufacturer in …
Custom backgrounds for your office team are not difficult to create, and they can be an instant professionalism …
A new study reveals that more than half of the British public regrets not discussing care home options …
First Time Mums UK is thrilled to announce its rapid expansion to a community of 75,000 members in …
Starting in the world of surfing is often the beginning of a passion. However, like in any beginning, …
Change is a constant in today’s dynamic business landscape, and effective leadership is essential for guiding organizations through …