Causes, Treatment, and Prevention of Gum Recession
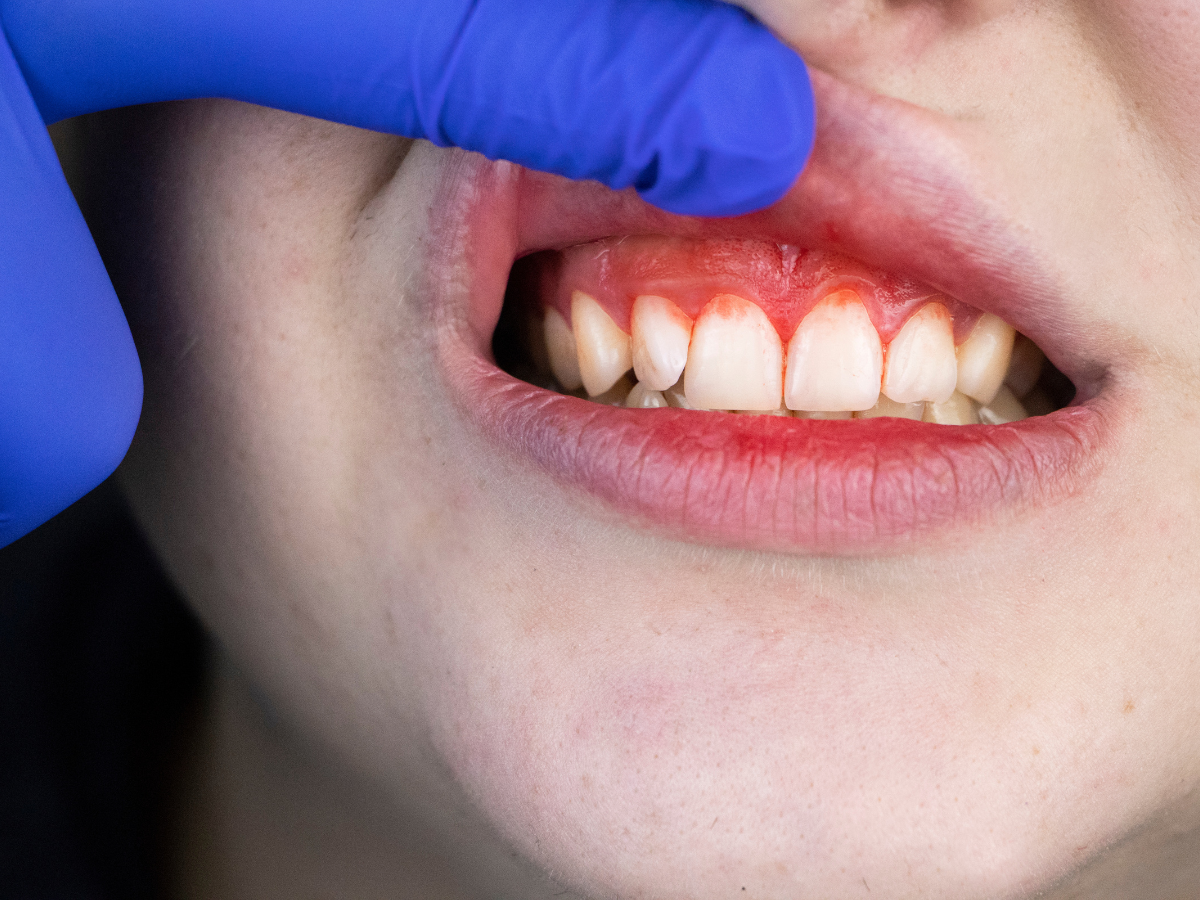
Gum recession is a condition where the gum tissue around the teeth begins to wear away or pull back, exposing more of a tooth’s root. It severely damages supporting gum tissue and eventually causes tooth loss if not treated. Pockets or gaps between the gum line and teeth develop, making it easier for disease-causing bacteria to grow and accumulate.
Receding gums are a common oral health problem, and it’s a gradual process most people don’t realize they already have. It usually begins with tooth sensitivity, or you might notice your teeth look longer. You may also feel a notch at the gum line.
Consult your dentist if you feel or notice your gums receding; do not ignore it. They have various ways of treating gum recession and preventing future damage.
Causes of Receding Gums
Receding gums occur due to various factors, including:
Periodontal Disease
Bacterial gum infections can damage the bones and tissues, keeping your teeth from falling out. It’s the primary cause of gum recession.
Genes
Certain people might be more vulnerable to gum diseases. Studies show that gum disease may predispose 30% of the population, regardless of how well they take care of their teeth.
Lack of Dental Care
Not brushing your teeth, flossing, or using antibacterial mouthwash makes it easier for plaque to turn into tartar. It’s a hard substance that builds up between your teeth only professional cleaning can remove. It can irritate your gums and cause gums to recede.
Hormonal Changes
Fluctuating female hormones in different stages of a woman’s life can make gums more sensitive to stimulus and increase the risk of gum recession.
Tobacco Products
People who smoke are more likely to have plaque that is difficult to remove, leading to gum recession.
Crooked Teeth
Crooked teeth put too much force on the gums and bone, damaging the teeth and gums and making gums recede.
How to Treat Receding Gums
Dentists determine how they treat receding gums based on their severity and your needs. Some of the ways they treat receding gums include:
Tooth Scaling and Root Planing
Your dentist may treat mild gum recession by deep cleaning the area. Deep cleaning, also known as tooth scaling and root planning, removes plaque and tartar from the teeth and roots below the gum line. Then, they smoothen the exposed root area to make it more difficult for bacteria to cling to your teeth. Dentists may also administer antibiotics to get rid of harmful bacteria.
Open Flap Scaling and Root Planing
Your dentist might decide against toot scaling and root planing if the pockets are too deep and if you have excessive bones. They might recommend surgery.
Open flap scaling and root planing is a surgery where a dentist or periodontist folds back the affected gum tissue to remove any bacteria buildup and secures the gum tissue over the root of the tooth to reduce the size of the pockets.
Regeneration
Your dentist or periodontist may recommend a procedure to regenerate bones if the bones supporting your teeth have been destroyed by gum recession.
After folding back the gum tissue and removing the bacteria, your dentist or periodontist may apply a regenerative material like a membrane, graft tissue, or tissue-simulating proteins to encourage natural bone and tissue regeneration. They then secure the gum tissue to the root of the tooth.
Soft Tissue Graft
Connective tissue transplant is one of the most common gum tissue graft procedures. It involves the removal of some of the subepithelial connective tissues underneath the skin of the roof of your mouth that are grafted onto gums surrounding an exposed tooth root.
A free gingival graft is another type of graft used to treat receding gums where they take tissue from the roof of the mouth, not just underneath the skin of your mouth’s roof.
How To Prevent Receding Gums
According to sunrise-dentistry.com, regular visits to the dentist for checkups and expert dental cleaning are excellent ways to prevent receding gums. Your dentist can identify early warning signs of gum disease even if you don’t have any symptoms. Smart oral hygiene habits are also an easy way to prevent gum disease. You might also want to reduce or quit smoking, eat a healthy diet, and monitor any changes in your mouth.
Regular flossing and brushing can remove bacteria, food particles, and plaque, but not tartar; professional dental cleaning is the only way to remove them. Tartar also causes recurring gum disease and receding gums, so consider having your teeth cleaned twice a year.
Key Takeaway
Receding gums are a common dental problem many people experience. Some of the factors that cause gum recession are genetics, poor dental care, hormonal changes, and periodontal disease. Fortunately, dentists have various ways of treating them, depending on the severity. Their treatments may include tooth scaling and root planing, bone regeneration, and soft tissue grafts.
It’s also easy to prevent gum recession by practicing good oral hygiene, quitting harmful habits like smoking, practicing a healthy diet, and visiting your dentist twice a year for a professional dental cleaning.