Wisdom Tooth Extraction 101: What You Need to Know
Getting your wisdom teeth removed can be daunting for any adult. But the truth is, wisdom tooth extraction is a fairly common procedure with few long-term risks. So if you’re considering getting your wisdom teeth extracted, it’s helpful to understand what to expect and the steps involved in the process.
As Casa Dental knows, wisdom teeth can be intimidating for many people. But have no fear: we’re here to give you a crash course on what to expect if you ever need to get your wisdom teeth removed. In this blog post, we’ll discuss wisdom teeth and explain the process of wisdom tooth extraction.
What are Wisdom Teeth & Why Do They Need to Be Extracted?
The teeth we commonly refer to as “wisdom teeth” are the final set of molars which appears between the ages of 17 and 25. They got their name because they often appear when considered more mature or ‘wise’.
Though not everyone has to have their wisdom teeth removed, they can be problematic for some individuals. Wisdom teeth can become impacted – meaning that other teeth or bones prevent them from erupting properly – leading to infection and gum disease if left untreated. In these cases, wisdom tooth extraction is necessary to avoid long-term damage.
How is a Wisdom Tooth Extracted?
Wisdom tooth extraction is the removal of one or more wisdom teeth. There are two main types of wisdom tooth extractions: surgery and non-surgery. In a surgical extraction, the surgeon will use special tools to remove the entire tooth, including its roots. Non-surgical extractions involve the removal of just the crown of a tooth that has already erupted through the gum line without cutting or drilling.
A dentist or an oral surgeon usually performs the extraction. Depending on the case’s complexity, you may be referred to a specialist for more complex wisdom tooth extractions.
Before a Tooth Extraction
Preparing for a wisdom tooth extraction begins with examining and evaluating the impacted teeth. The dentist will take X-rays to determine the exact location of the teeth and evaluate them for any signs of infection or decay.
Before your procedure, you may be given an anaesthetic to numb the area around the affected tooth. Depending on the complexity of your case, anaesthesia may also include general anaesthesia (to make you unconscious), local anaesthesia (to numb just the area around your wisdom tooth) or a combination of both.
During a Tooth Extraction
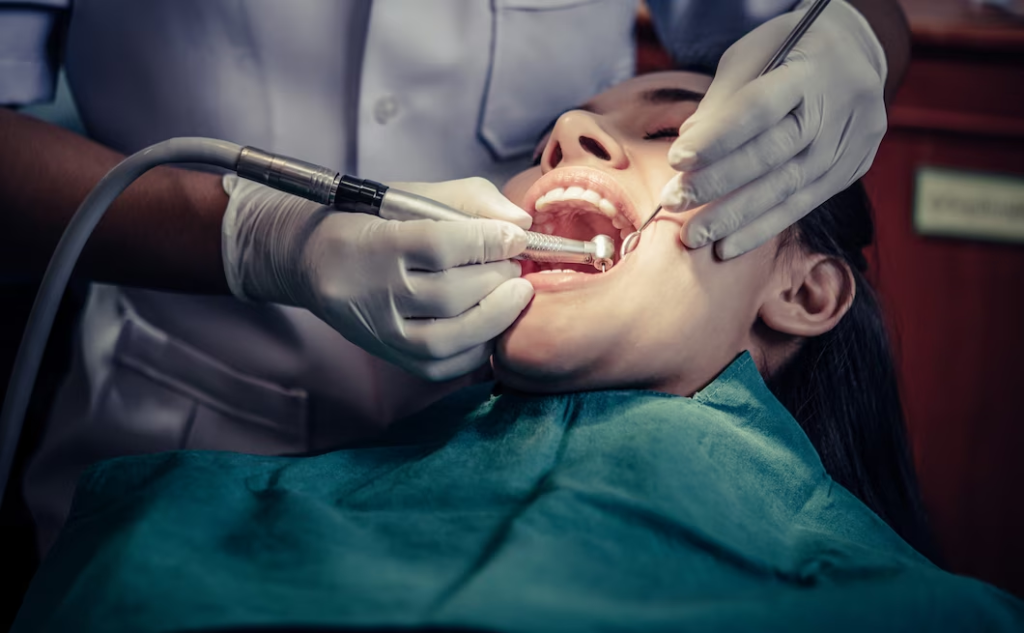
As the anaesthesia takes effect, the dentist will use special tools to loosen and remove the tooth. The entire process usually takes about 15-30 minutes.
Step 1 – Incision
The first step of the extraction process is to make an incision in the gum tissue to access and remove the wisdom tooth. Depending on your needs, this incision may be made through the gums or around the lip.
Step 2 – Tooth Removal
Next, the dentist will use special instruments to loosen the tooth from the bone and remove it. Depending on your needs, they may need to cut away some of the gum tissue covering the wisdom tooth.
Step 3 – Cleaning of the Extraction Site
Once the tooth is removed, the dentist will clean the area to remove debris. This is an important step because it helps prevent infection and promote healing.
Step 4 – Stitching the Wound
The dentist may stitch the wound closed to help it heal properly. This helps reduce swelling and discomfort and also promotes faster healing. Following your dentist’s instructions for post-operative care after a wisdom tooth extraction, including using an ice pack, taking pain medication as prescribed and avoiding vigorous activities for several days afterwards, is important.
Step 5 – Gauze Placement
Finally, the dentist will place a gauze pad over the extraction site and ask you to bite down on it for 15-20 minutes. This helps reduce bleeding and encourages clotting at the extraction site.
The process may differ slightly if looking into a non-surgical extraction option. In a non-surgical extraction, the dentist will use forceps to gently remove the tooth from its socket. There is no incision required and no stitching afterwards.
After the Procedure
When the procedure is complete, you may experience pain and discomfort as your mouth adjusts to its new normal. Here are a few tips for managing post-extraction care:
- Take any prescribed medications as directed
- Apply an ice pack to help with swelling
- Avoid vigorous activities or those that put pressure on your jaw
- Rest and relax the area around the extraction site
- Rinse gently with warm salt water to reduce swelling and help keep the area clean
- Eat soft foods that won’t cause further irritation or injury to the extraction site
- Return for follow-up appointments with your dentist or oral surgeon.
Advantages of Extracting Wisdom Tooth
There are several advantages of having your wisdom teeth removed. First, it can help reduce the risk of gum disease, cavities and other dental problems that wisdom teeth can cause if they come in incorrectly or remain impacted in the jawbone. Removing them before they become a problem can also help keep your mouth healthy and free from infection or decay.
Additionally, removing wisdom teeth can make cleaning and maintaining your oral health easier since you won’t have to worry about brushing and flossing around an extra set of molars. Finally, removing your wisdom teeth can also improve overall comfort by relieving pain caused by overcrowding or misalignment.
Conclusion
Wisdom teeth can cause various issues if they come in incorrectly or become impacted. That’s why talking to your dentist about the potential risks and benefits of extracting them is important. The extraction process is relatively straightforward, but you should always follow your dentist’s instructions for post-operative care. With proper care, you can ensure that your mouth remains healthy and free from infection or decay.
If you’re considering removing your wisdom teeth, talk to your dentist today about the best option. Your dentist can answer any questions and help you through the extraction process.

